How Manufacturing Errors in Progressive Lenses Impact Wearer Satisfaction
What Every Optical Lab Needs to Know
- The Crucial Role of Precision in Progressive Lens Manufacturing
- How Lens Manufacturing Errors Impact Wear Satisfaction: Key Study Findings
- Phase I: First Impressions—What Wearers Think Right Away
- Phase II: Seven-Day Adaptation—Long-Term Use and User Experience
- Phase III: Comparative Evaluation—Choosing the Best Option
- Key Findings: Why Manufacturing Errors Matter for Progressive Lenses
- The Business Case for Improved Quality Control in Lens Manufacturing
- Raising the Standards for Lens Manufacturing Precision
- Download the Full Poster

How Manufacturing Errors in Progressive Lenses Impact Wearer Satisfaction
What Every Optical Lab Needs to Know
In optical manufacturing, precision isn’t just a requirement—it’s the foundation of every high-performance lens. Free-form progressive lenses (PPLs), are designed to deliver flawless vision across near, intermediate, and far distances. But even minor deviations in the lens manufacturing process can lead to noticeable issues in wearers’ satisfaction. This article breaks down the study findings on how common lens manufacturing errors affect progressive lens users.
The Crucial Role of Precision in Progressive Lens Manufacturing
Progressive lenses (PPLs) are designed to seamlessly transition between multiple focal lengths. Errors during manufacturing—such as those caused by improper generator calibration or suboptimal parameter inputs—can introduce distortions that affect visual performance. These errors often go undetected during standard quality control checks, as they focus only on specific reference points.
In this study, two types of manufacturing errors were examined:
- Dot Errors (DE): These are localized bumps in curvature that disrupt smooth vision, averaging 0.33 ± 0.29 D with an extension of 4.3 ± 2.8 mm.
- Ring Errors (RE): These create a curvature ring that can impair peripheral vision, with a mean diameter of 22.6 ± 7.7 mm and a deviation of 0.14 ± 0.07 D.
- Although these errors met ISO 8980-2 tolerances, their impact on wearers’ perception can be far reaching.
- Explore: Guide to Optical Lenses: The Science Behind How They Work
How Lens Manufacturing Errors Impact Wear Satisfaction: Key Study Findings
This three-phase study examined how these errors influenced wearer satisfaction across different stages of lens use. To measure the effects of these errors, the researchers conducted a double-masked observational study with 36 presbyopic participants experienced in wearing progressive lenses. Subjects tested two sets of lenses—one with manufacturing errors and one without - under controlled conditions.
Effects of Errors at Reference Points
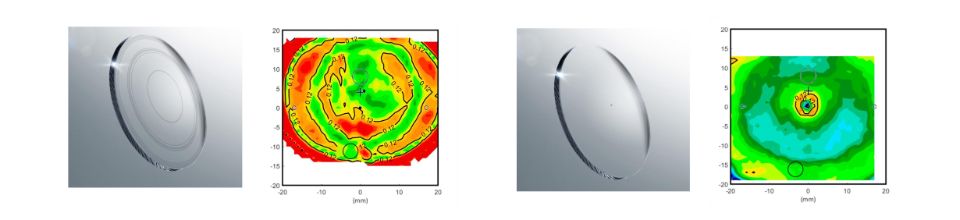
Figure 1: Error maps of both types of induced errors: rings (left) and dots (right).
Phase I: First Impressions—What Wearers Think Right Away
In this stage, participants rated their lenses (on a scale of 1–5) for near, intermediate, and far distances and overall vision immediately after trying them.
Phase II: Seven-Day Adaptation—Long-Term Use and User Experience
After wearing each pair of lenses for seven days, participants evaluated their experience, particularly when viewing electronic devices and engaging in daily activities.
Phase III: Comparative Evaluation—Choosing the Best Option
Using a randomized complete block design, participants selected the lenses that provided better overall visual performance.
Key Findings: Why Manufacturing Errors Matter for Progressive Lenses
The study revealed distinct differences in user satisfaction based on the type of error:
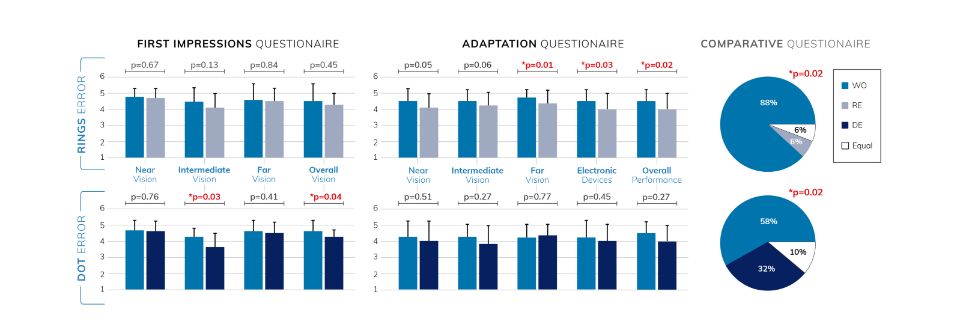
- Dot Errors (DE): Participants testing lenses with dot errors reported significantly lower satisfaction with intermediate vision and overall performance during first impressions.
- Ring Errors (RE): Over time, participants using lenses with ring errors noted decreased satisfaction, particularly when using electronic devices and in far-distance vision tasks.
When asked to compare the two lens types:
- 58% of participants testing DE lenses preferred the error-free design, while 10% found both lenses comparable.
- 88% of participants testing RE lenses favored the error-free design, while 6% found both lenses comparable.
The study revealed distinct differences in user satisfaction based on the type of error:
Dot Errors (DE): Participants testing lenses with dot errors reported significantly lower satisfaction with intermediate vision and overall performance during first impressions.
Ring Errors (RE): Over time, participants using lenses with ring errors noted decreased satisfaction, particularly when using electronic devices and in far-distance vision tasks.
When asked to compare the two lens types:
58% of participants testing DE lenses preferred the error-free design.
88% of participants testing RE lenses favored the error-free design.
The Business Case for Improved Quality Control in Lens Manufacturing
This research underscores the critical role of precision in free-form lens manufacturing. Dot errors (central errors) affect first impressions, while ring errors (peripheral errors) influence long-term satisfaction. For optical labs, investing in advanced calibration methods and thorough quality checks is a strategic move that can significantly enhance wearers' overall experience.
By detecting and correcting these subtle errors early, labs can improve product quality, reduce customer dissatisfaction, and ultimately boost brand loyalty.
Raising the Standards for Lens Manufacturing Precision
The evidence is clear: the smallest manufacturing errors in progressive lenses can lead to significant declines in wearer satisfaction. To stay competitive and deliver optimal user experiences, optical labs must adopt stricter quality control processes that catch both central and peripheral errors early. The future of lens manufacturing depends on this level of commitment to precision.
Download the Full Poster
Explore the detailed findings of our study on the impact of manufacturing errors in progressive lenses and their influence on wearer satisfaction. This poster delves into the methodology, data analysis, and insights into how central (dot) and peripheral (ring) errors affect user perception and overall lens performance. Discover how enhancing quality control processes in lens manufacturing can lead to better visual outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.






